Blog
Recent Posts
Introduction To The NMEA 2000 Marine Networking Standard
Posted by on

NMEA 2000 is a marine networking standard created and administered by the National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA). The NMEA is an association of marine electronics manufacturers, dealers, and technicians.
The NMEA 2000 standard describes a low-cost, moderate capacity, bi-directional, multi-transmitter, multi-receiver instrument network. Typical data on a network using this standard include position latitude and longitude, GPS status, steering commands to autopilots, waypoint lists, wind sensor data, engine sensor data, depth sounder sensor data, and battery status data.
NMEA 2000 is the most consequent and straightforward adaptation of SAE J1939. NMEA 2000 is a modernized version and replacement of an older standard, NMEA 0183. It has a sinificantly higher data rate (250k bits/second vs. 4.8k bits/second for NMEA 0183). It also uses a binary message format as opposed to the ASCII serial communications protocol used by NMEA 0183. Another distinction between the two protocols is that NMEA 2000 is a multiple-talker, multiple-listener data network, whereas NMEA 0183 is a single-talker, multiple-listener serial communications protocol.
More Resources
- What is NMEA 2000? (PDF)...
- NMEA 2000 Explained (PDF)...
- The Basics of NMEA 2000 (Boating Magazine)...
- NMEA 2000 (Wikipedia)...
- NMEA 0183 vs. NMEA 2000...
- What is the Difference Between SAE J1939 and NMEA 2000?
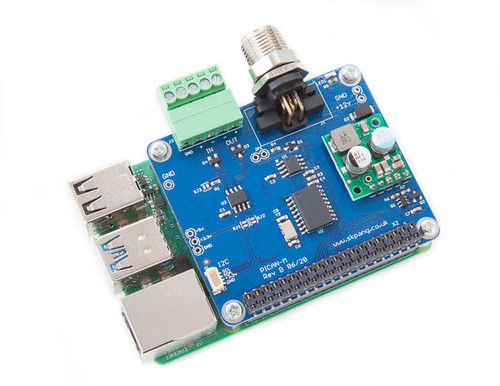
PICAN-M - NMEA 0183 & NMEA 2000 HAT For Raspberry Pi
The PICAN-M (M = Marine) is a Raspberry Pi HAT with NMEA 0183 and NMEA 2000 connection. The NMEA 0183 (RS422) port is accessible via a 5-way screw terminal. The NMEA 2000 port is accessible via a Micro-C connector.
The board comes with a 3A SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply), allowing to power the Raspberry Pi plus HAT from an onboard power source (12 VDC).
Industrial Ethernet Guide - Ethernet and TCP/IP Basics
The following is part of A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet by Wilfried Voss.Note: This chapter can only provide a rudimentary overview of the underlying Ethernet technology. There are already a significant number of works on TCP/IP available (see also the “References” appendix) that explain the topic in great detail.Nevertheless, the information in this chapter is [...]
Industrial Ethernet Guide - The OSI Reference Model
The following is part of A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet by Wilfried Voss. The OSI Reference Model is at the heart of serial networking technologies, including Industrial Ethernet. The understanding of the model is mandatory, not only when it comes to understanding Ethernet TCP/IP, the underlying technology of Industrial Ethernet; it also serves as a model explaining how the different [...]
Industrial Ethernet Guide - Client/Server Vs. Master/Slave
The following is part of A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet by Wilfried Voss.Note: There is an ongoing discussion regarding the political correctness of the term "Master/Slave", specifically in the United States, due to its history. While the author would welcome a revised, standardized term, the industry and the various standardization organizations have been slow to [...]
Industrial Ethernet Guide - Network Topologies
The following is part of A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet by Wilfried Voss.Distributed Control, and the advantages that come with it, is best demonstrated through the classic, lean Bus network structure. There are, however, several different network topologies that serve virtually the same purpose but, at the same time, have their individual characteristics that are [...]
Latest Developments In Automotive Ethernet Technology And Implementation
Learn about the latest developments in automotive Ethernet technology and implementation with this fully revised second edition. Including approximately twenty-five percent new material and greater technical detail, coverage is expanded to include: Detailed explanations of how the 100BASE-T1 PHY and 1000 BASE-T1 PHY technologies actually work A step-by-step description of how the 1000BASE-T1 channel was derived A summary of [...]
Home Security Network Development Using The Arduino Platform
The Arduino is an open source micro-controller built on a single circuit board that is capable of receiving sensory input from the environment and controlling interactive physical objects. It is also a development environment that allows the writing of software to the board, and is programmed in the Arduino programming language. It is used for a variety [...]
ARM Cortex M4 Computing Platform With FreeRTOS For Modbus / TCP Remote Digital I/O Applications
Artila Electronics, a designer and manufacturer of embedded device networking and computing, released their RIO-2015PG, a FreeRTOS programmable remote I/O module. The RIO-2015PG is powered by a 32-bit Atmel SAM4E16E 120MHz ARM Cortex M4 processor, which comes with 256KB SRAM, 3MB Flash and the FreeRTOS real time operating system. The industrial I/O of RIO-2015PG features [...]
Automotive Ethernet Expected to Gradually Replace Traditional CAN Bus Network Backbone
I recently looked into the not-so-new SAE J1939-22 Standard, which promises to solve the bandwidth issue with Classical CAN. I am a little late addressing the topic since we offer a few SAE J1939 products, such as our SAE J1939 ECU Simulator combined with our JCOM1939 Monitor Software for Windows. Nevertheless, we are working on a new [...]
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...