Blog
Recent Posts
Programming the ESP32: Choosing the Right IDE for Your Workflow
Posted by on
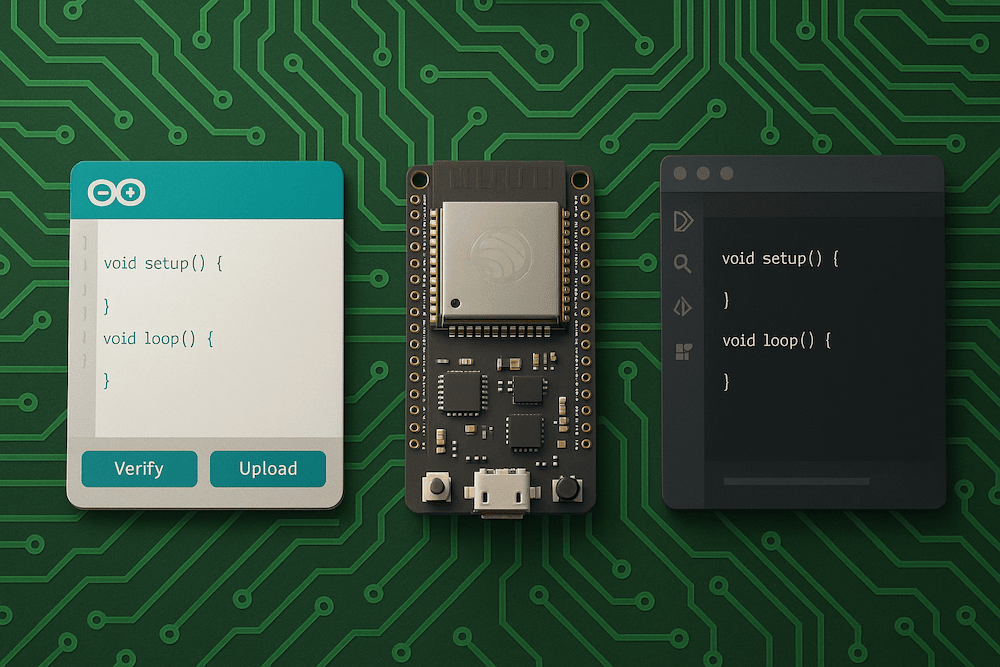 The ESP32 has become one of the most versatile and affordable microcontrollers available today. Whether you’re building IoT devices, automation systems, or experimenting with wireless communication, the ESP32 provides exceptional power and flexibility—dual-core processing, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, low-power modes, and robust GPIO capabilities.
The ESP32 has become one of the most versatile and affordable microcontrollers available today. Whether you’re building IoT devices, automation systems, or experimenting with wireless communication, the ESP32 provides exceptional power and flexibility—dual-core processing, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, low-power modes, and robust GPIO capabilities.
But before any code can run on an ESP32, developers must decide how to program it—and that usually starts with choosing the right Integrated Development Environment (IDE). The IDE determines not only how you write and upload code but also how you debug, visualize data, and manage projects over time.
Two environments dominate the ESP32 ecosystem: the Arduino IDE and Espressif’s own IDE (based on Eclipse or Visual Studio Code through the ESP-IDF). Each caters to a different type of developer, offering distinct advantages in usability, structure, and performance.
The Arduino IDE: Simplicity Meets Accessibility
The Arduino IDE remains the most popular platform for ESP32 programming, and with good reason. Originally designed to make microcontroller development approachable for beginners, it has evolved into a surprisingly powerful environment capable of handling complex projects.
Advantages of Using the Arduino IDE
-
Ease of Use
-
The interface is clean and intuitive—code editor on top, serial monitor on the bottom, and just two key buttons: Verify and Upload.
-
There’s little configuration needed, allowing you to focus on writing logic instead of managing toolchains.
-
-
Extensive Library Support
-
The Arduino ecosystem boasts thousands of libraries for sensors, displays, communication protocols, and more.
-
Many of these libraries are compatible with ESP32, meaning developers can reuse familiar Arduino code with minimal changes.
-
-
Large Community and Examples
-
The sheer size of the Arduino community means endless tutorials, example sketches, and troubleshooting help.
-
Beginners can find inspiration in ready-made projects while advanced users can explore custom modules and hardware integration.
-
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility
-
Works seamlessly on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
-
The same sketch can typically run on an ESP32, Arduino Mega, or even a Nano with small adjustments.
-
-
Serial Monitoring and Plotting
-
The built-in Serial Monitor and Serial Plotter provide a simple way to visualize sensor data and debug real-time operations—especially valuable for IoT and robotics applications.
-
-
Low Learning Curve
-
The “sketch-based” model (setup/loop) makes it easy to prototype quickly. Even complex Wi-Fi or Bluetooth examples can be compiled and uploaded in minutes.
-
When the Arduino IDE Shines
-
Rapid prototyping and proof-of-concept work.
-
Educational environments and maker spaces.
-
Projects emphasizing hardware experimentation over complex software architecture.
The Arduino IDE’s simplicity is its greatest strength—but it’s also its limitation for large-scale or performance-sensitive applications.
The Espressif IDE (ESP-IDF): Power, Control, and Professional Development
For developers who need more control and a deeper understanding of what’s happening inside the ESP32, Espressif’s official development framework—the ESP-IDF (IoT Development Framework)—offers a professional-grade toolchain.
Espressif provides multiple interfaces for working with ESP-IDF, the most common being:
-
Espressif IDE (Eclipse-based)
-
VS Code Extension for ESP-IDF
Both options wrap the same framework in different user interfaces, giving developers flexibility in how they interact with the underlying system.
Advantages of Using Espressif IDE
-
Full Hardware Control
-
ESP-IDF provides access to all of the ESP32’s subsystems—task scheduling, memory management, interrupts, power states, and dual-core operation.
-
You can fine-tune the hardware far beyond what’s available through Arduino abstractions.
-
-
Professional Project Structure
-
Instead of a single “sketch,” ESP-IDF projects are modular and folder-based, ideal for collaboration and version control.
-
The structure encourages scalable development, where drivers, components, and application logic are clearly separated.
-
-
Integrated Debugging Tools
-
Supports step-by-step debugging, breakpoints, and variable inspection through JTAG and OpenOCD integration.
-
This makes it easier to locate subtle timing issues, memory leaks, or task collisions in multi-threaded applications.
-
-
Optimized Performance
-
Developers can directly use FreeRTOS APIs (built into ESP-IDF), enabling precise control of multitasking and real-time behavior.
-
This is essential for robotics, motor control, or industrial IoT systems requiring predictable execution.
-
-
Long-Term Maintainability
-
Projects built with ESP-IDF can scale from prototypes to commercial production with minimal rework.
-
Espressif continuously updates the framework to support new chips and security features, ensuring longevity.
-
-
Extensive Documentation
-
Espressif’s documentation portal offers in-depth explanations of each subsystem, configuration file, and API.
-
Though more technical, it empowers developers to understand the why behind each setting.
-
When Espressif IDE Excels
-
Professional and large-scale projects.
-
Applications requiring multi-core or real-time tasking.
-
Developers who need fine-grained performance tuning and debugging.
-
Teams working under version control and CI/CD systems.
While it demands a steeper learning curve, the Espressif IDE rewards persistence with unmatched insight and power.
Choosing Between Arduino IDE and Espressif IDE
The choice ultimately depends on your goals:
| Project Type | Recommended IDE | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Hobby projects, quick prototypes | Arduino IDE | Fast setup, abundant examples, minimal configuration |
| Educational and classroom use | Arduino IDE | Accessible for all skill levels |
| Commercial IoT or firmware development | Espressif IDE / ESP-IDF | Scalability, debugging, performance tuning |
| Projects requiring FreeRTOS multitasking | Espressif IDE | Direct access to RTOS primitives |
| Community-driven open-source projects | Arduino IDE | Easier collaboration with makers and hobbyists |
Many developers start with Arduino to validate concepts and then transition to ESP-IDF once projects demand more structure and control. This gradual evolution mirrors the learning curve of embedded development itself.
A Balanced Perspective
Both environments coexist for a reason. The Arduino IDE democratized embedded programming, lowering the barrier to entry for millions of creators. Meanwhile, Espressif’s IDE pushes the boundary for what’s possible on low-cost hardware, enabling products once reserved for far more expensive platforms.
In practice, your choice may not be permanent. Many experienced developers maintain both environments—using Arduino for quick testing and ESP-IDF for production work. Each tool brings its own rhythm to the creative process.
Conclusion
The ESP32 is more than just a microcontroller; it’s a bridge between the maker world and professional embedded engineering. The Arduino IDE offers simplicity and immediate results. The Espressif IDE provides depth and precision.
Whichever path you choose, the ESP32 rewards curiosity and experimentation. The IDE is merely your canvas—the innovation, as always, lies in the code you create.
 From smart sensors to cloud integration and the realm of TinyML, this book is your complete guide to the IoT ecosystem—built around the ESP32 and industry-standard tools.
From smart sensors to cloud integration and the realm of TinyML, this book is your complete guide to the IoT ecosystem—built around the ESP32 and industry-standard tools.
Key Features
-
Build fully functional IoT projects from the ground up using the ESP32
-
Customize solutions, connect them to the cloud, visualize real-time data, and implement robust security
-
Gain hands-on experience through practical projects, including an audio player, smart home system, and more
Book Description
The ESP32, a low-cost and energy-efficient system-on-chip microcontroller, has become the foundation of countless Wi-Fi–enabled devices, driving the next generation of IoT innovation.
This book presents a comprehensive, end-to-end approach to designing, developing, and deploying IoT systems with the ESP32—covering everything from data acquisition and communication to cloud integration and real-time visualization.
You’ll start with IoT fundamentals and real-world applications before diving into device construction using the ESP32. Each chapter adds a new layer of capability, exploring sensor communication, LittleFS and LVGL libraries, Wi-Fi connectivity, security protocols, and Grafana-based data visualization.
A dedicated section introduces AI and Machine Learning for embedded systems, demonstrating how to build and deploy TinyML applications on the ESP32-S3, enabling you to create intelligent, next-generation embedded products.
By the end of this book, you’ll have gained the practical skills to develop professional-grade IoT solutions. The final chapters culminate in a Smart Home project, uniting all the learned concepts into a cohesive, real-world system. More information...
Embedded CAN Bus Development with the ESP32 Processor
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a robust communication protocol designed to facilitate data exchange between microcontrollers and devices in automotive and industrial applications. With its high reliability and real-time capabilities, it has become a cornerstone in modern embedded systems. The ESP32, a popular microcontroller from Espressif Systems, offers integrated CAN controller support, making [...]
ESP32 Programming - Classical CAN to Bluetooth Gateway
In this post, I will present a CAN to Bluetooth gateway based on the ESP32 processor. The above image shows my test setup using our ESP32 WiFi, Bluetooth Classic, BLE, CAN Bus Module, a CAN-Bus Hub With 7 Ports And DC Power Connection, and the PCAN-USB Pro. As its description implies, the ESP32 module provides all necessary [...]
Do NOT Install ESP32 by Espressif Systems Version 3.0-alpha1
Today, I experienced a little scare. As usual, I opened the Arduino IDE on my Windows-11 machine, and as a first action, I allowed the recommended updates. Not suspecting any significant problems, I added some code and compiled it, only to end up with multiple error messages. I found nothing wrong with the code I had [...]
ESP32, ESP32-S2 - Serial Port, Native USB Access
The test setup, as shown in the image, represents the hardware of a new project that requires reading CAN (Controller Area Network) data frames, combining them with real-time information plus GPS position, and storing the result onto an SD card. This post will focus on the ESP32 communicating with the GPS module delivering NMEA 0183 [...]
J1939 Protocol Stack Sketch for ESP32 Using the Arduino IDE
The ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system-on-chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power management modules. Furthermore, the processor provides the means to easily [...]
ESP32 Triple CAN Bus Application Through Adding Two MCP2515 Ports
The first question that may arise when talking about accessing the MCP2515 CAN Bus controller per ESP32 may be, "Why would you need an MCP2515 controller when the ESP32 comes with an internal CAN port?" Yes, I found this question in one of the online forums while researching this particular topic. The answer is easy: [...]
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
