Blog
Recent Posts
Optimized Design: Enhancing CAN Transceiver Isolation for Reliable Fieldbus Networks
Posted by on
 The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus has become a staple in industrial automation, process control, medical systems, and manufacturing due to its high noise immunity and error-handling capabilities. As CAN networks often span long distances and connect multiple systems, isolating the bus from individual systems is critical. Isolation prevents electrical transients, eliminates ground loops, and enhances overall system reliability. This article explores CAN’s physical layer, the necessity of system isolation, and the functional role of isolated CAN transceivers.
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus has become a staple in industrial automation, process control, medical systems, and manufacturing due to its high noise immunity and error-handling capabilities. As CAN networks often span long distances and connect multiple systems, isolating the bus from individual systems is critical. Isolation prevents electrical transients, eliminates ground loops, and enhances overall system reliability. This article explores CAN’s physical layer, the necessity of system isolation, and the functional role of isolated CAN transceivers.
CAN Bus Protocol and Arbitration
CAN operates as a two-wire serial communication bus standardized under ISO 11898. It employs a carrier-sense multiple access (CSMA) mechanism with collision detection and message priority arbitration (CD+AMP). Each node monitors the bus before transmission. If multiple nodes attempt transmission simultaneously, arbitration is resolved through dominant (logic low) and recessive (logic high) bit priorities.
Messages are structured as data frames, encapsulating identification, control, data, error-checking, and acknowledgment fields. The protocol’s arbitration ensures that high-priority messages gain immediate access without data loss.
Signal Levels and Cable Considerations
CAN transceivers utilize differential signaling with open-drain output stages. During dominant transmission, both output transistors engage, creating a voltage differential. In recessive mode, pull-up resistors maintain a balanced voltage level.
Cable length directly impacts data rate. ISO11898 specifies a maximum of 40 meters at 1 Mbps, with longer distances possible at reduced data rates. Twisted-pair cables with 120Ω impedance are standard, and termination resistors at each end mitigate reflections. Stub lengths should be minimized to prevent signal degradation.
Need for Isolation
Industrial CAN networks are susceptible to noise from ground loops and electrical surges. Ground loops arise when nodes at different locations reference local grounds, causing potential differences and unintended currents. Electrical surges, induced by switching equipment, electrostatic discharge (ESD), or lightning strikes, can compromise network integrity.
Galvanic isolation protects against these issues by decoupling the network from node circuitry. Modern digital isolators achieve up to 4 kV of peak isolation and transient immunity up to 50 kV/µs, ensuring reliable operation.
Digital Isolators and Isolated CAN Transceivers
Digital isolators employ capacitive isolation barriers to transfer signals across nodes. High-speed channels (100 kbps to 150 Mbps) transmit pulses directly, while low-speed channels (
Traditional digital isolators lack differential signaling, requiring placement on the single-ended side of a CAN transceiver. Modern isolated CAN transceivers integrate isolation barriers with enhanced transceiver capabilities, including:
-
Over-temperature and over-voltage protection (-27V to 40V)
-
Common-mode range of -12V to 12V
-
Voltage transient tolerance from -200V to 200V
-
Dominant-time-out circuits to prevent network blockage due to hardware or software failures
Conclusion
The introduction of fully integrated isolated CAN transceivers significantly improves network protection against electrical transients. Texas Instruments and other manufacturers offer robust digital isolators and transceivers that enhance CAN reliability in demanding applications.
By adopting isolated CAN transceivers, engineers can ensure more resilient and interference-free fieldbus designs for industrial and automation environments.
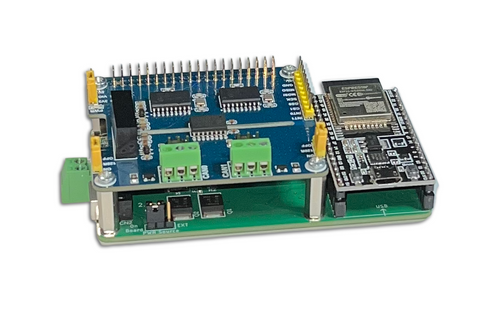 ESP32 Development Board with Dual Isolated CAN Bus HAT
ESP32 Development Board with Dual Isolated CAN Bus HAT
The espBerry DevBoard seamlessly integrates the ESP32-DevKitC development board with any Raspberry Pi HAT via its onboard RPi-compatible 40-pin GPIO header. Rather than serving as a Raspberry Pi replacement, the espBerry enhances the ESP32’s functionality, leveraging the extensive ecosystem of RPi HATs and their diverse hardware options.
Designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, particularly those demanding wireless connectivity, the espBerry offers a powerful and flexible solution. Developers can easily utilize open-source code samples within the Arduino IDE, benefiting from its intuitive programming environment and extensive support. More information...
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
