Blog
Recent Posts
Adafruit HUZZAH32 ESP32 Feather Board – WiFi, Bluetooth & Battery Power for IoT Projects
Posted by on
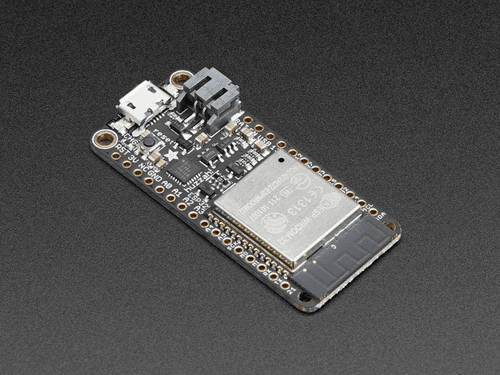 The Adafruit HUZZAH32 Feather Board brings Espressif’s powerful ESP32-WROOM32 module into Adafruit’s popular Feather ecosystem. It offers built-in WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity, dual-core performance, and efficient battery management — making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) and embedded applications that demand portability, wireless communication, and reliability.
The Adafruit HUZZAH32 Feather Board brings Espressif’s powerful ESP32-WROOM32 module into Adafruit’s popular Feather ecosystem. It offers built-in WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity, dual-core performance, and efficient battery management — making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) and embedded applications that demand portability, wireless communication, and reliability.
Compact Power for Wireless Projects
The HUZZAH32 is based on the ESP32 dual-core Tensilica LX6 processor running at up to 240 MHz. It delivers robust computing performance with approximately 600 DMIPS, enabling multitasking, network handling, and real-time control in parallel.
It includes 520 KB of internal SRAM and 4 MB of onboard SPI flash memory, providing sufficient resources for most wireless applications such as environmental monitoring, automation, or control systems.
The integrated 2.4 GHz WiFi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth (Classic + BLE) support allow for seamless connectivity to networks, mobile devices, and peripherals. Whether you are streaming sensor data, controlling relays, or building wearable prototypes, the HUZZAH32 simplifies wireless integration.
Feather Form Factor and Compatibility
Adafruit’s Feather design emphasizes modularity and expandability.
The HUZZAH32 maintains full compatibility with Adafruit FeatherWings — add-on boards that provide displays, relays, sensors, and communication interfaces.
This makes it easy to build custom IoT systems without soldering complex wiring harnesses or redesigning PCBs.
The board measures approximately 51 mm × 23 mm × 12 mm, small enough for portable and embedded enclosures.
Power Management and Battery Operation
A major strength of the HUZZAH32 lies in its built-in Li-Po/Li-ion charging circuit and 3.3 V low-dropout regulator, allowing flexible power sources:
-
5 V via USB input,
-
3.7 V from a rechargeable Li-Po battery,
-
or both simultaneously, with automatic charging when USB is connected.
The “BAT” pin provides battery voltage output for low-power sensors, while the “USB” and “EN” pins help developers measure and control power consumption.
Although the ESP32 chip supports extremely low-power deep sleep, actual current draw depends on the board’s regulator and charger circuitry. Developers targeting ultra-low-power designs should measure current consumption in their specific setup.
Input/Output Capabilities
The board provides flexible digital and analog interfacing options:
-
12 × ADC channels for analog sensors
-
2 × DAC outputs for analog signal generation
-
Multiple UART, SPI, and I²C interfaces
-
10 × capacitive touch inputs
-
PWM outputs on most pins for LED or motor control
It also includes a built-in Hall sensor and an ultra-low-noise amplifier, expanding its potential for sensor-based projects.
Because not all ESP32 features are preconfigured in the Arduino environment, users who need additional serial ports or advanced peripherals may need to modify their code or use the Espressif ESP-IDF for full control.
Software Environments
The HUZZAH32 supports multiple programming options:
-
Arduino IDE: Simplifies setup and programming for hobby and maker projects.
-
ESP-IDF: Espressif’s professional development framework, offering full hardware access and FreeRTOS support.
-
CircuitPython: Adafruit’s Python-based environment for rapid prototyping without compilation.
Example sketches are available for WiFi scanning, web servers, Bluetooth beacons, and low-power modes, helping users get started quickly.
Wireless Connectivity
The integrated 2.4 GHz WiFi radio supports both client and access-point modes, making it suitable for direct device-to-device or networked communication. The onboard PCB trace antenna delivers solid range for most applications, but placement and orientation affect signal quality — best results are achieved with minimal metal nearby.
Bluetooth Classic and BLE functionality open further opportunities, such as wireless data transfer, smartphone control interfaces, or sensor beacons.
Practical Applications
-
IoT Sensor Nodes – For temperature, humidity, or motion sensors sending data to cloud servers.
-
Home and Building Automation – Wireless control of lighting, fans, and security devices.
-
Portable Data Loggers – Battery operation with integrated charging for remote monitoring.
-
Prototyping with FeatherWings – Rapid expansion through compatible add-on boards.
-
Educational and Research Projects – Ideal for experimenting with wireless networking and microcontroller programming.
Performance Notes and Limitations
-
Operates exclusively at 3.3 V logic levels; connecting 5 V peripherals can damage the device.
-
The PCB antenna limits extreme range; external antenna versions are better suited for long-distance communication.
-
Deep-sleep current is higher than bare ESP32 modules due to additional components.
-
4 MB flash memory may be insufficient for very large applications or multiple OTA update images.
-
Advanced users may benefit from ESP-IDF to utilize dual-core multitasking and real-time scheduling.
Getting Started Tips
-
Install the ESP32 board package in the Arduino IDE.
-
Select Adafruit HUZZAH32 from the Tools → Board menu.
-
Upload the Blink example to verify setup.
-
For battery use, connect a 3.7 V Li-Po via the JST connector.
-
Use 2.4 GHz WiFi networks; 5 GHz bands are not supported.
-
Keep the antenna area clear of metal or conductive surfaces.
For long battery life, disable unused peripherals and make use of deep sleep cycles between transmissions.
Conclusion
The Adafruit HUZZAH32 Feather Board strikes an excellent balance between performance, power efficiency, and modularity.
Its dual-core processor, built-in WiFi and Bluetooth, and FeatherWing compatibility make it one of the most versatile development boards for IoT and embedded design.
Whether you’re building a battery-powered environmental sensor, a wireless control module, or a portable prototype, the HUZZAH32 provides a dependable foundation backed by Adafruit’s strong documentation and community support.
Product Summary
-
Processor: Dual-Core 240 MHz LX6
-
Memory: 520 KB SRAM, 4 MB Flash
-
Connectivity: WiFi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth Classic + BLE
-
Power: 3.3 V logic, Li-Po charging circuit
-
Dimensions: 51 × 23 × 12 mm
-
Price: $9.95
 Internet of Things Projects with ESP32: Build exciting and powerful IoT projects
Internet of Things Projects with ESP32: Build exciting and powerful IoT projects
The ESP32, a low-cost MCU with integrated Wi-Fi and BLE capabilities, comes with a variety of modules and development boards for building IoT applications efficiently. Wi-Fi and BLE are standard network stacks for Internet-of-Things applications providing cost-effective solutions for your business and project requirements.
This book is a fundamental guide for developing ESP32 programs and starts by explaining GPIO (General Purpose I/O) programming with sensor devices. The reader gets up to speed with ESP32 development through several IoT projects such as weather stations, sensor loggers, smart homes, Wi-Fi cams, and Wi-Fi wardriving. The reader learns how to use ESP32 boards to facilitate interactions between mobile applications and cloud servers, such as AWS.
By the end of this book, you'll have learned how to control a range of IoT projects using the ESP32 chip.
Learning Python and Electronics with the ESP32
In an age where smart devices are seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, the demand for accessible tools to understand and build electronics projects has never been greater. This book aims to demystify both Python programming and basic electronics, serving as a comprehensive introduction for beginners. Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, educator, or simply curious [...]
Harnessing the Power of the ESP32-S3: A Look at Copperhill’s CAN FD Development Board
In the evolving landscape of IoT, industrial automation, and automotive communication, the demand for a versatile, wireless-enabled microcontroller with CAN bus capabilities has never been greater. Copperhill Technologies rises to the occasion with its latest innovation—a development board based on the ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N8R8, engineered to support both Classical CAN and CAN FD protocols. At the heart of [...]
Exploring the ESP32 Processor and Its CAN Interface Programming
The ESP32 processor, developed by Espressif Systems, has rapidly emerged as a favorite among developers and hobbyists alike due to its robust performance, integrated wireless connectivity, and versatility in handling various tasks. Among its many features is a built-in CAN (Controller Area Network) interface—technically implemented as a TWAI (Two-Wire Automotive Interface) controller—that has opened up [...]
ESP32 Processor: CAN Bus Topology and Termination Resistors
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32. It is my experience that newcomers to the technology overlook the importance of termination resistors. Missing or misplaced resistors can lead to transmission errors or even prevent transmission altogether. The general rule is that if you connect to an existing, fully [...]
ESP32 Development Kits with Onboard CAN Bus Controller
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system-on-chip microcontroller with integrated WiFi and dual-mode Bluetooth. It is equipped with a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in dual-core and single-core versions. The microcontroller features built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifiers, low-noise receive amplifiers, filters, and power management modules. It is the successor to the ESP8266 SoC. There are [...]
ESP32 Processor: Adding CAN/CAN-FD Controllers per SPI Port
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32. The internal CAN controller SJA1000 does not support CAN-FD and is not CAN-FD tolerant. To use CAN-FD with the ESP32, you need to employ CAN-FD breakout boards that are accessible per the ESP32’s SPI ports. Note: The SPI ports are not [...]
ESP32 Processor: Internal SJA 100 CAN Bus Controller
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32.The ESP32 integrates a CAN Bus controller compatible with the NXP SJA1000. Thus, it is CAN 2.0B (ISO 11898, a.k.a. Classical CAN) specification-compliant.As with the SJA1000, the ESP32 CAN Bus controller provides only the data link layer and the physical layer [...]
ESP32 Processor: Adding a CAN Bus Transceiver
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32.As a quick reference, I want to address the need for a CAN transceiver. As mentioned in the previous chapter, the ESP32 has an internal CAN Bus controller. However, this doesn't mean you can directly connect it to a network. You [...]
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data Rate)
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32. CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data Rate) is an extension of the original CAN bus protocol. It was created to provide increased bandwidth within automotive and industrial networks. It brings application software closer to "real-time" by minimizing delays between instruction [...]
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
