Blog
Recent Posts
C Programming For The Internet-Of-Things (IoT) Under Linux
Posted by on
Applying C is the book you need if you are programming for Single Board Computers (SBCs) that operate under Linux, or if you perform any coding in C that interacts with the hardware. As there is not the right name for this body of knowledge, it is not easy to find a single source for it. This book collects all of these low-level, hardware-oriented, and often hardware-specific ideas. As such, it is a reasonably advanced book. This is not to say that it is difficult, but it does assume that you already know how to program in C and that you know the essential idioms of C.
Starting from the straightforward task of making a program run automatically, we look at how your program works with user-mode Linux. If you are working with hardware, arithmetic cannot be ignored, and separate chapters are dedicated to integer, fixed-point, and floating-point arithmetic. Equally, to handle I/O you need to have a solid grasp of files and the pseudo-file system. The dev/mem file, coupled with memory-mapped files, makes it possible to work with raw memory without leaving user mode. Sockets are a general-purpose method of communicating over networks and related infrastructure, and here the focus is on transmitting data over the internet. For this, we build a web client and a server.
Next, we examine graphics, which you might find unusual in a book on small systems, but these days even small systems have GPUs, and graphics come as standard. It is customary to think of adding low-cost output devices such as 7-segment displays to IoT devices. Still, with low-priced HDMI/DVI displays available, it becomes cost-effective to use the built-in graphics hardware in a straightforward approach.
After this, we turn to the idea of multi-tasking using Pthreads. As well as looking at threads, we contemplate locking, using mutex and condition variables, and scheduling. Although interrupts do not exist in user-mode Linux, we can get very close using poll and threading. Now that multiple cores are a feature of even low-cost SBC, in later chapters, we cover managing cores, look at C11’s atomics and introduce its memory models and barriers. Finally, we take a quick look at how to incorporate assembler with C.
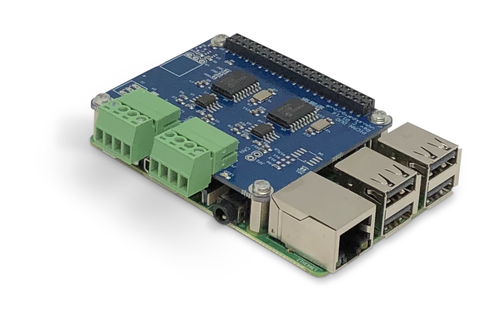
Raspberry Pi 3 B+ System With Dual CAN Bus Interface
The Raspberry Pi 3 System With Dual CAN Bus Interface (PiCAN2-DUO) comes with a pre-installed Raspbian operating system.
The system is equipped with a PiCAN2 DUO board, depending on the selected option, with or without SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply). The SMPS allows the powering of the whole system, i.e. the Raspberry Pi and the PiCAN board, per external power connection (e.g. the 12 VDC supply in a vehicle).
The Raspberry Pi 3 B+ is equipped with a high-performance heatsink set to reduce chip hot-spots and to increase the thermal dissipation surface area.
The PiCAN2 DUO board provides Controller Area Network (CAN) Bus capabilities for the Raspberry Pi. It uses the Microchip MCP2515 CAN controller with MCP2551 CAN transceiver. Connection are made via 4-way screw terminals.
There is an easy-to-install SocketCAN driver, and programming can be accomplished in C or Python.
ARM Cortex M4 C Programmable Remote I/O Module With FreeRTOS
Artila Electronics launched the FreeRTOS programmable remote I/O module, RIO-2014PG. Example programs which demonstrate serial and Ethernet data communication, which demonstrates how to push sensor data to IBM Bluemix using MQTT is also included for sensor to cloud application development. Low power consumption of ARM Cortex M4 plus efficiency of FreeRTOS make RIO-2014PG an light weight computing [...]
Guide To Full-Fledged Electronic Prototyping Using The Arduino Platform
In just 24 sessions of one hour or less, Sams Teach Yourself Arduino Programming in 24 Hours teaches you C programming using the Arduino, so you can start creating inspired “DIY” hardware projects of your own! Using this book’s straightforward, step-by-step approach, you will walk through everything from setting up your programming environment to mastering C syntax [...]
Applying Test Driven Development (TDD) to Embedded C
Another day without Test-Driven Development (TDD) results in time wasted with chasing bugs and watching your code deteriorate. You thought TDD was for someone else, but it's not; it's for you, the embedded C programmer. TDD helps you prevent defects and effectively build software with a long useful life. This is the first book to [...]
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...