Recent Posts
Classical CAN (CC), the Original CAN Bus Technology
Posted by on
This post is an excerpt from our application note Controller Area Network (CAN) Development with ESP32.
Note: The term “Classical CAN” was introduced in the ISO 11898-1: 2016 Standard.
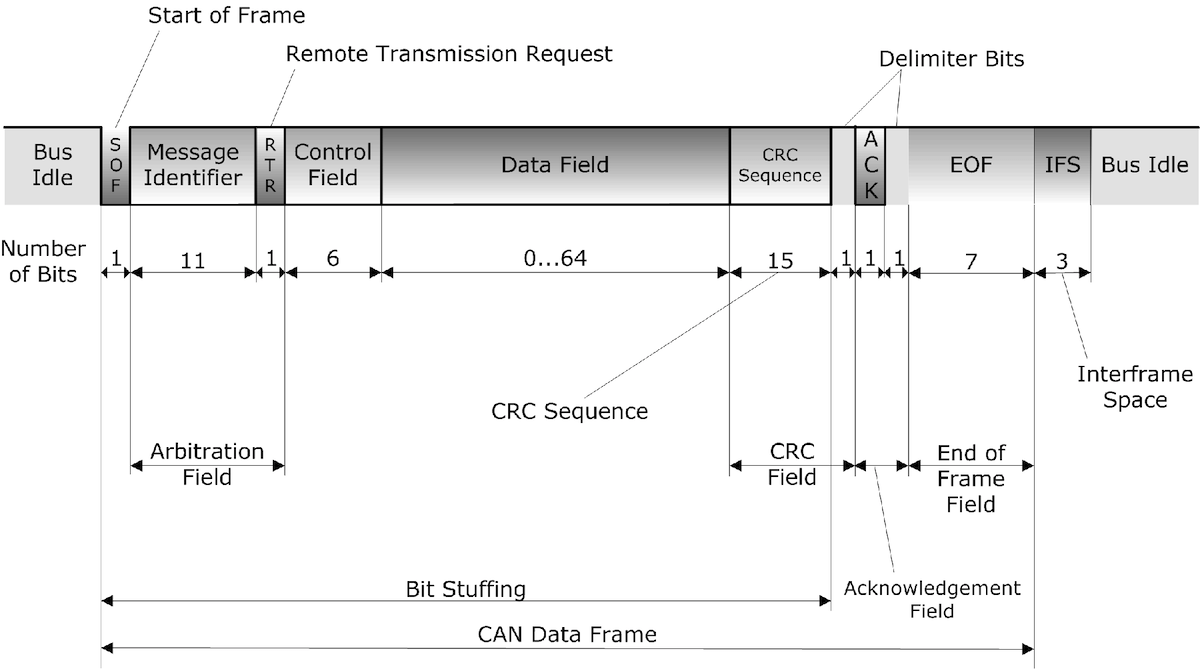
Classical CAN represents the basis for CAN FD (and CAN XL), meaning they share the same features and advantages, as explained in the previous chapter. While CAN FD adds more functionality and communication speed, its controllers can act exactly like Classical CAN, supporting the features listed here:
Classical CAN
- Is a serial networking technology for embedded solutions.
- Needs only two wires named CAN_H and CAN_L.
- Operates at data rates of up to 1 Megabit per second.
- Supports a maximum of 8 bytes per message frame.
- Does not support node IDs, only message IDs. One application can support multiple message IDs.
- Supports message priority, i.e., the lower the message ID the higher its priority.
- Supports two message ID lengths, 11-bit (standard) and 29-bit (extended).
- Does not experience message collisions (as they can occur with other serial technologies).
- Is not demanding in terms of cable requirements. Twisted-pair wiring is sufficient.
Note: For more detailed information on Classical CAN, please refer to A Comprehensible Guide to Controller Area Network.
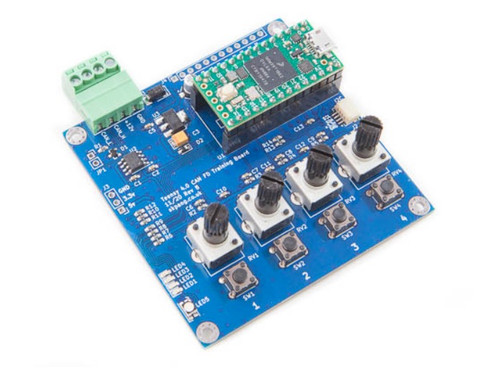
Teensy 4.0 CAN Bus And CAN FD Training Board
his board features an Arduino-compatible Teensy 4.0 microprocessor system. It serves as a training board for CAN Bus and CAN FD. It comes equipped with four onboard potentiometers, LEDs, an RGB LED, and switches. The board is capable of simulating analog inputs and transmitting the signal to the CAN bus in either Classical CAN or CAN FD format. It is powered by an external +12 VDC feed with reverse voltage protection. External sensors can be connected via the QWIIC connector. More Information...
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...