Recent Posts
ECU Simulator Generates Eleven Most Frequently Used SAE J1939 Signals For Diesel Engines
Posted by on
The Au J1939 Simulator 1.00A Value Package non-plus Edition generates 11 most frequently used SAE J1939 signals for Diesel Engines. The device supports multiple CAN Bus baud rates (1M/500K/250K/125K/62.5K bps) and can be configured in the field to cover the new SAE 500K CAN Bus baud rate.
Supported SAE J1939 Parameters (PGN) And Features:
- Engine % Load at Current Speed
- Engine Oil Pressure (PSI)
- Engine Coolant Temperature
- Engine Fuel Rate
- Engine Speed (RPM)
- Engine Total Hours of Operation (Hr) *
- Response for Engine Hour Request (Rx)
- Engine Address Claiming
- Engine Address CANNOT Claim
- Response for Address Claim Request (Rx)
- Address Conflict Response with Contention
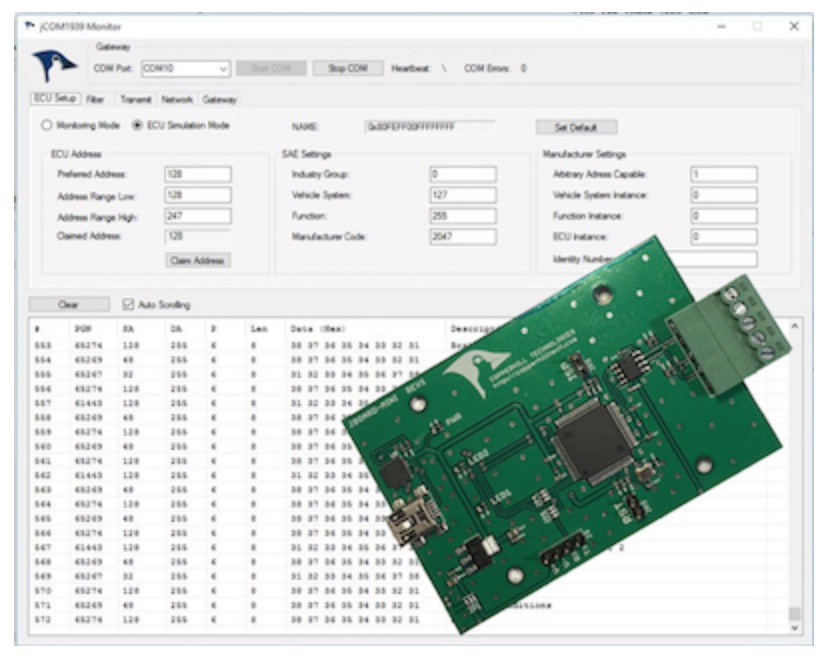
SAE J1939 ECU Simulator Board With USB Port
The jCOM.J1939.USB gateway board is a high-performance, low-latency vehicle network adapter for SAE J1939 applications. It allows any host device with a USB COM port to monitor SAE J1939 data traffic and communicate with the SAE J1939 vehicle network.
The board supports the full SAE J1939 protocol according to J1939/81 Network Management (Address Claiming) and J1939/21 Transport Protocol (TP). It is also supported by an extensive programming interface for Windows and Linux/Ubuntu applications, including full C/C++/C# source code for short time-to-market developments.
The strength of the board lies in the fact that the entire SAE J1939 protocol, including all timing requirements, is stored on-chip, thus taking the burden off the main system. The board uses a USB COM port to communicate with the main system, i.e. all data transfer is handled through a standard COM port access.
The communication protocol between the board and the main system is well documented and thus allows a porting to any computer system with a USB connection. Working source code libraries exist for Windows (C# under Visual Studio 2012/2013), Linux and its derivatives (C++ using Code::Blocks), and Raspberry Pi (C using the standard gcc compiler).
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...