Blog
Recent Posts
Mastering CAN Bus: Essential Guide to Understanding and Troubleshooting Vehicle Networks
Posted by on
 In today’s world of connected vehicles and industrial automation, understanding the details of networked communication protocols has become a pivotal skill for engineers and technicians alike. The book Mastering CAN Scratch: Understanding & Troubleshooting (ISBN/ASIN B0G24Z25RZ) steps into this space by offering a comprehensive, hands-on guide to the widely used Controller Area Network (CAN) bus and its associated troubleshooting methodologies. It takes the reader from the fundamentals—what a CAN bus is, how it physically and logically operates, typical wiring and bus architectures—through to more advanced diagnostic techniques including fault isolation, signal integrity issues, node conflicts and data error conditions. What makes it stand out is its “scratch-from-first-principles” approach: rather than assuming prior mastery, the author invites you to build your understanding from the ground up, making it suitable for both newcomers and seasoned professionals looking to refresh or expand their CAN bus troubleshooting toolkit.
In today’s world of connected vehicles and industrial automation, understanding the details of networked communication protocols has become a pivotal skill for engineers and technicians alike. The book Mastering CAN Scratch: Understanding & Troubleshooting (ISBN/ASIN B0G24Z25RZ) steps into this space by offering a comprehensive, hands-on guide to the widely used Controller Area Network (CAN) bus and its associated troubleshooting methodologies. It takes the reader from the fundamentals—what a CAN bus is, how it physically and logically operates, typical wiring and bus architectures—through to more advanced diagnostic techniques including fault isolation, signal integrity issues, node conflicts and data error conditions. What makes it stand out is its “scratch-from-first-principles” approach: rather than assuming prior mastery, the author invites you to build your understanding from the ground up, making it suitable for both newcomers and seasoned professionals looking to refresh or expand their CAN bus troubleshooting toolkit.
What truly elevates the book is its real-world orientation. Rather than purely theoretical descriptions, it includes case studies and practical workflows: how to detect bus conflicts using oscilloscopes, how to interpret error-frames under different fault conditions, how to systematically approach intermittent/cold-start faults and how to modify or validate node firmware settings to eliminate elusive problems. The author also dedicates attention to emerging variants and enhancements of the CAN protocol—so you’re not just learning “old school” classical CAN, but gaining insight into how to troubleshoot modern implementations that may incorporate CAN FD, higher bit-rates, and complex multi-ECU networks. For anyone working in vehicle diagnostics, embedded system design or industrial control networks, this book is a valuable addition to the reference shelf—and, with its clear writing and structured progression, a very practical learning resource. More information...
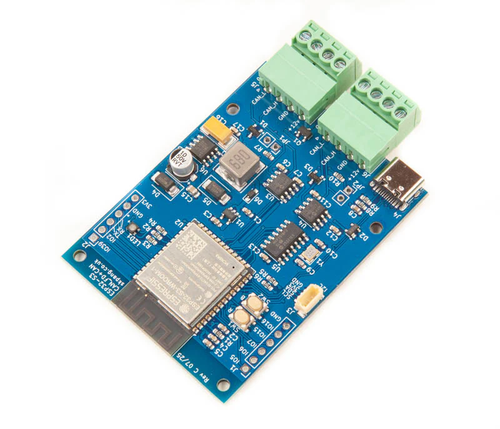 ESP32S3 Board with CAN FD and Classical CAN Ports
ESP32S3 Board with CAN FD and Classical CAN Ports
The board is built around the ESP32-S3‑WROOM‑1‑N8R8 module, giving it Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5 (including LE and mesh) and a dual-core Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 processor up to 240 MHz. It also packs 8 MB of quad-SPI flash and 8 MB of PSRAM, making it capable of fairly heavy embedded workloads. On the connectivity side, this board supports classical CAN (Controller Area Network) via the ESP32-S3’s built-in CAN controller, and extends to CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) using an external MCP2518FD SPI-based controller plus high-speed CAN transceivers. The board is powered by a 7 V–24 V input through an onboard SMPS with reverse-polarity protection, features a USB-C connector for power and native USB OTG programming/debugging, and includes convenient extras like boot/reset buttons, an I²C expansion port, and an RGB LED for status indication.
From an application standpoint, the board is tailored for scenarios where robust in-vehicle or industrial networking meets wireless/edge processing. Because it supports both classical CAN and CAN FD, it is well-suited for bridging legacy CAN networks with next-generation high-bandwidth CAN FD systems — for instance, automotive diagnostics, industrial automation gateways, or IoT devices that aggregate sensor data via CAN and then upload it wirelessly via Wi-Fi or BLE. The native USB support simplifies programming and debugging compared to boards that require a separate USB-UART chip. In short, it presents a flexible platform for embedded engineers working at the intersection of networked control buses and wireless edge intelligence. More information...
OBD-2 Automotive Code Encyclopedia and Cross-Reference Guide
The OBD-2 Automotive Code Encyclopedia and Cross-Reference Guide By Mandy Concepcion presents information without the sponsoring of any one particular company or organization. No endorsements are made or implied. Any reference to a company or organization is done purely for the sake of information.You gain access to a series of valuable cross-reference automotive sensor values, [...]
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
