Blog
Recent Posts
NMEA 2000: A Comprehensive Overview and Integration with Copperhill PiCAN-M Series
Posted by on
 NMEA 2000 (National Marine Electronics Association 2000) is a standardized communication protocol used in the marine industry to facilitate seamless data exchange between electronic devices onboard vessels. Based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol (ISO 11898), NMEA 2000 enables efficient, real-time data sharing between sensors, navigation instruments, and control systems. This standard has been widely adopted due to its robustness, ease of integration, and ability to support multiple devices on a single network.
NMEA 2000 (National Marine Electronics Association 2000) is a standardized communication protocol used in the marine industry to facilitate seamless data exchange between electronic devices onboard vessels. Based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol (ISO 11898), NMEA 2000 enables efficient, real-time data sharing between sensors, navigation instruments, and control systems. This standard has been widely adopted due to its robustness, ease of integration, and ability to support multiple devices on a single network.
Origin and Evolution of NMEA 2000
The National Marine Electronics Association developed the NMEA 2000 standard as an upgrade to its predecessor, NMEA 0183. While NMEA 0183 relied on serial communication and point-to-point connections, NMEA 2000 introduced a multi-drop network topology with higher data rates (250 kbps) and better fault tolerance. This improvement significantly reduced wiring complexity, enhanced reliability, and improved interoperability among marine electronic devices. Over time, the adoption of NMEA 2000 has expanded beyond marine applications into other industries requiring robust and real-time data communication.
Key Features of NMEA 2000
-
CAN-based Communication: Uses a reliable and widely adopted Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol.
-
Plug-and-Play Connectivity: Simplifies integration and expansion by allowing devices to be easily added or removed from the network.
-
Multi-Device Support: Enables multiple devices such as GPS, engine monitoring systems, depth sounders, and autopilots to communicate on the same network.
-
Higher Data Rate: Operates at 250 kbps, allowing for real-time data exchange with minimal latency.
-
Reliable and Fault-Tolerant: Includes features like message prioritization and error checking to ensure data integrity.
-
Standardized Protocol: Ensures interoperability among different manufacturers, reducing compatibility issues.
Applications of NMEA 2000
NMEA 2000 is predominantly used in marine environments, but its robust networking capabilities make it suitable for various applications:
1. Marine Navigation and Monitoring
-
Integration of GPS receivers, chart plotters, and autopilots.
-
Real-time engine monitoring and performance analytics.
-
Communication between depth sounders, fish finders, and sonar systems.
2. Commercial and Recreational Vessels
-
Fleet management and remote diagnostics.
-
Fuel efficiency monitoring and optimization.
-
Integration of weather sensors and wind instruments.
3. Autonomous and Smart Marine Systems
-
Unmanned surface vessels (USVs) for scientific and military applications.
-
Smart buoy monitoring systems.
-
Advanced data analytics for predictive maintenance.
Copperhill PiCAN-M Series for NMEA 2000 Integration
Copperhill Technologies offers the PiCAN-M series, which is designed to facilitate NMEA 2000 communication using Raspberry Pi-based systems. These add-on boards leverage the CAN bus protocol, making them an ideal solution for marine and industrial applications requiring reliable networking.
Features of PiCAN-M Series
-
Integrated NMEA 2000 Compatibility: Direct connection to NMEA 2000 networks without additional converters.
-
Raspberry Pi-Based Expansion: Enables cost-effective and flexible development for marine applications.
-
CAN Bus Interface: Supports high-speed data transmission and real-time network communication.
-
Python and C++ Support: Allows for easy development of custom applications and data logging.
-
Power Supply via NMEA 2000: Eliminates the need for external power sources in certain setups.
Implementing PiCAN-M for NMEA 2000 Applications
The PiCAN-M series is particularly useful for engineers, researchers, and hobbyists looking to integrate NMEA 2000 networks with Raspberry Pi. Below are some example applications:
-
Marine Data Logging System
-
The PiCAN-M board can collect and store data from multiple sensors such as GPS, depth sounders, and engine monitors.
-
Using Python scripts, data can be processed and displayed on a dashboard or stored in a database for later analysis.
-
-
Real-Time Vessel Monitoring
-
Raspberry Pi, combined with PiCAN-M, can act as a centralized monitoring system for boats, aggregating data from various NMEA 2000 devices.
-
This system can provide alerts, performance reports, and fuel efficiency analysis.
-
-
Smart Autopilot Systems
-
The PiCAN-M can facilitate communication between navigation sensors and autopilot systems, enabling better route optimization and autonomous navigation.
-
Conclusion
NMEA 2000 has revolutionized marine electronics by providing a standardized and reliable communication framework. With its CAN-based architecture, it ensures seamless integration of multiple devices, making it a preferred choice for navigation, monitoring, and automation in marine applications. The Copperhill PiCAN-M series further enhances NMEA 2000’s capabilities by allowing Raspberry Pi-based systems to interface with marine networks, enabling cost-effective and flexible solutions for real-time monitoring and data analytics. By leveraging these technologies, marine engineers and developers can create innovative applications that improve vessel performance, safety, and efficiency.
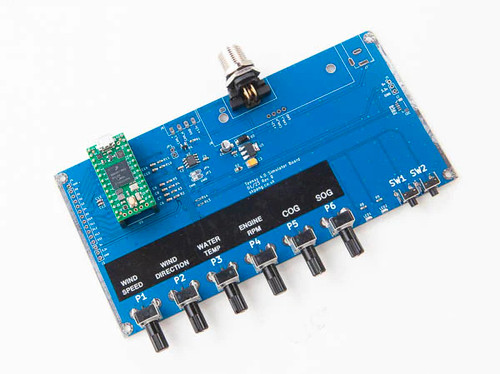 Teensy 4.0 NMEA 2000 Simulator
Teensy 4.0 NMEA 2000 Simulator
The NMEA 2000 Simulator utilizes the Teensy 4.0 module (included in the package) for bench-testing NMEA 2000 devices. It allows for real-world testing by simulating network activity. Users can adjust six PGNs via potentiometers and control two additional PGNs using onboard switches. Additionally, we provide open-source firmware, enabling users to modify and expand the supported NMEA 2000 PGNs to suit specific testing needs.
About NMEA 2000
NMEA 2000 is a standardized marine networking protocol developed and maintained by the National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA), a consortium of marine electronics manufacturers, dealers, and technicians.
This protocol defines a cost-effective, bi-directional, multi-transmitter, and multi-receiver instrument network based on Controller Area Network (CAN) technology. It facilitates seamless data exchange between marine devices, including GPS systems, autopilots, wind sensors, engine monitors, depth sounders, and battery management systems. Common data transmitted over an NMEA 2000 network include:
- GPS position (latitude & longitude)
- Navigation status
- Autopilot steering commands
- Waypoint lists
- Wind and weather sensor data
- Engine and depth sensor data
- Battery voltage and power status
By leveraging NMEA 2000, marine electronics can achieve better interoperability, reduced wiring complexity, and real-time data sharing, enhancing vessel performance and safety. More information...
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
