Recent Posts
RS232 to USB Converter With Arduino Due Or Mega 2560
Posted by on
 Just about everyone who is involved with serial communication will have his/her RS232 to USB converter. Today's PCs don't even bother to support RS232. Consequently, a USB converter is mandatory to monitor RS232 data traffic. All this appears to render the following project obsolete. However, when it comes to a protocol converter, i.e. the conversion of data frames, this solution might come in handy.
Just about everyone who is involved with serial communication will have his/her RS232 to USB converter. Today's PCs don't even bother to support RS232. Consequently, a USB converter is mandatory to monitor RS232 data traffic. All this appears to render the following project obsolete. However, when it comes to a protocol converter, i.e. the conversion of data frames, this solution might come in handy.
Note: I am also preparing a post addressing an RS485 to USB converter, which will allow to read protocols such as Modbus or SAE J1708/1587 and, consequently, allow filtering and modifications of data frames.
For my test and development scenario I have used the Arduino Mega 2560, but the sketch will also run on the Arduino Due. Both boards provide three additional serial ports (UARTs) of which I used one to connect our RS232 Breakout Board.
Before we get into more details, let me address a few obstacles (dealing with serial ports using the Arduino platform can be annoying when you need to spend time to investigate undocumented limitations):
The Arduino Due's programming port is limited to a baud rate of 115,200 baud. I haven't found out in detail where the limitation stems from (I am not a hardware specialist), but my suspicion is that it is a combination of hardware (UART-to-USB converter) and software (OS shortcomings) restrictions. There is a little trick to push the baud rate to 230,400. For more information on the topic refer to the following posts:
- Arduino Due: Using the Serial Monitor At 230400 Baud...
- ARM Cortex Processors - UART Programming Problem at Baud Rates Higher Than 115200...
In case you need higher communication speeds using the Arduino Due, see also my post:
The additional three serial ports on the Arduino Due and Arduino Mega 2560 run only reliably up to 115200 baud. A baud rate of 230400 is possible but you have to deal with random data loss. My assumption (without looking at the processor data sheets) is that the processors are able to support higher baud rates but only with using handshake signals such as CTS and RTS, which are not directly supported by either system. It is most probably possible to create CTS/RTS per GPIO but I wasn't ready to spend the extra effort.
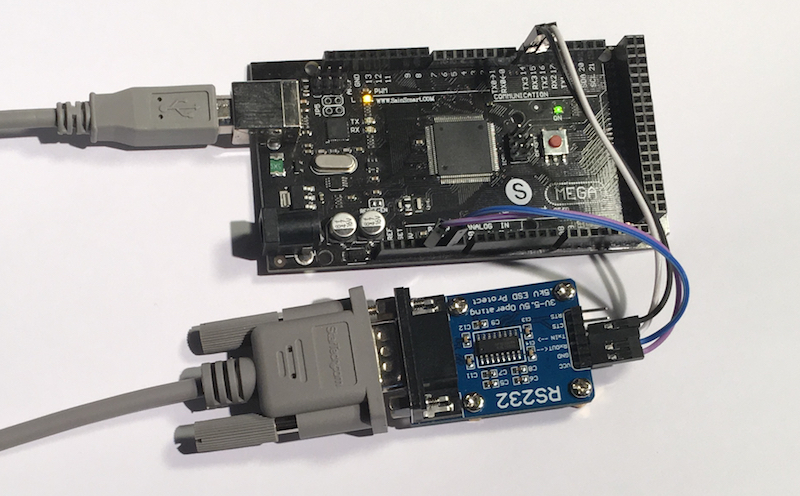
Connecting the RS232 Breakout Board

The above image shows the connection to the three additional serial ports (UARTs), which is identical between the Arduino Mega 2560 and Arduino Due. See also the image below identifying the power connection on the Arduino:

I established the connection between the Arduino and the RS232 Breakout Board as follows:
Arduino RS485 Board
5V ------> VCC
GND ------> GND
RX3 ------> RxOut
TX3 ------> TxIn
I chose the RX3/TX3 connection just by chance; all serial ports work the same way, but it must reflect in the software, of course.
The corresponding Arduino sketch is fairly simple - and, of course, can be modified as easily:

Please feel free to contact me through the Contact Us page on this website in case you have questions or comments.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...

