Recent Posts
Learning Python and Electronics with the ESP32
Posted by on
 In an age where smart devices are seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, the demand for accessible tools to understand and build electronics projects has never been greater. This book aims to demystify both Python programming and basic electronics, serving as a comprehensive introduction for beginners. Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, educator, or simply curious about the world of embedded systems, this book offers a hands-on journey that requires no prior experience in programming or electronics.
In an age where smart devices are seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, the demand for accessible tools to understand and build electronics projects has never been greater. This book aims to demystify both Python programming and basic electronics, serving as a comprehensive introduction for beginners. Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, educator, or simply curious about the world of embedded systems, this book offers a hands-on journey that requires no prior experience in programming or electronics.
At its heart, the book centers around the ESP32, a powerful microcontroller that has become a cornerstone in the maker community due to its affordability, versatility, and built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. By combining the ESP32 with Python—a widely-used and beginner-friendly programming language—learners are empowered to quickly move from blinking an LED to creating functional IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
The ESP32 Microcontroller: An Overview
Developed by Espressif Systems, the ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system-on-a-chip (SoC) with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. It’s an upgrade to its predecessor, the ESP8266, offering more GPIO pins, higher processing power, and greater flexibility for a wide range of applications.
The ESP32 is well-suited for both prototyping and production-level designs. It comes in various forms, but this book focuses primarily on two of the most widely used variants: the ESP32 DevKit v1 and the ESP32 Lite. These boards provide users with easy access to GPIO pins, making it straightforward to connect sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
What makes the ESP32 particularly attractive is its native support for MicroPython, a lightweight version of Python designed to run on microcontrollers. This opens the door for people who are more comfortable with high-level programming to develop embedded applications without diving into the complexities of C or C++.
Python as a Learning Language
Python has surged in popularity for good reason—it’s readable, intuitive, and powerful. This book adopts Python as its primary programming language not only because of its syntax simplicity but also due to the existence of MicroPython, which brings Python's ease-of-use into the embedded systems world.
In the early chapters, the book introduces Python programming through practical and engaging examples. One such example is the construction of a Morse Code encoder, which helps learners grasp the core elements of Python such as variables, loops, conditional statements, and functions. These foundational concepts are explored in a way that prioritizes experimentation and discovery.
As readers progress, they are taught how to structure their Python code using functions and modules, enabling them to write reusable and maintainable code. Key data structures like lists and dictionaries are also explored, offering powerful tools to manage and manipulate information within a program.
Getting Started: Setting Up the ESP32 and Thonny
Before diving into coding, learners are guided through the process of flashing MicroPython firmware onto the ESP32 board. This involves erasing the default firmware and installing the MicroPython interpreter, allowing the ESP32 to execute Python code directly.
To write and upload programs to the board, the book introduces the Thonny Python IDE, a beginner-friendly development environment that streamlines coding, debugging, and file transfers to the ESP32. Thonny offers a clean interface and integrated tools that reduce the friction often experienced when working with microcontrollers.
Building Circuits and Writing Code
In the electronics portion of the book, readers learn how to construct basic circuits using a breadboard. Clear diagrams are provided for both the ESP32 Lite and DevKit v1, ensuring compatibility and clarity for a range of hardware setups.
Through hands-on projects, readers are introduced to key electronic components:
-
LEDs and resistors, for basic output
-
Push buttons and sensors, for user input and environmental interaction
-
Servo motors, to introduce motion control
-
OLED displays, for presenting real-time information
Each project is accompanied by Python code that demonstrates how to read from and write to the ESP32’s GPIO pins. The combination of hardware and software provides a well-rounded introduction to physical computing.
Exploring the Internet of Things (IoT)
One of the ESP32’s most compelling features is its built-in Wi-Fi capability. This opens the door to numerous IoT applications, from home automation to remote monitoring systems. The final chapters of the book explore this potential by teaching readers how to:
-
Connect the ESP32 to a Wi-Fi network
-
Host a web server on the ESP32 to serve HTML content or control devices from a browser
-
Use the ESP32 to call web APIs, allowing it to retrieve live data from the Internet, such as weather updates or stock prices
These projects not only demonstrate the power of the ESP32 but also prepare learners for real-world applications, giving them the foundation to develop their own network-connected devices.
Conclusion
This book is more than just a technical manual—it’s an invitation to explore, create, and innovate. By combining the accessible syntax of Python with the robust capabilities of the ESP32, readers are equipped with the tools and knowledge to build interactive and intelligent systems from scratch.
Whether you dream of building smart gadgets, automating your home, or diving into the world of IoT, this book provides the ideal starting point. With patience, practice, and curiosity, you’ll find that learning Python and electronics with the ESP32 is not just educational—but truly empowering. More information...
ESP32 WiFi, Bluetooth Classic, BLE, CAN Bus Module
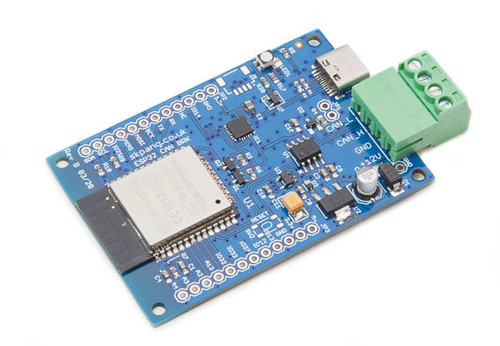 The ESP32 CAN-Bus Module brings together wireless and wired communication capabilities on a compact and powerful development board. At its core is the ESP32-WROOM-32 module, featuring a dual-core Xtensa LX6 processor running at up to 240 MHz, supported by 520 KB of SRAM and 4 MB of flash memory. This enables robust performance for a wide range of embedded applications.
The ESP32 CAN-Bus Module brings together wireless and wired communication capabilities on a compact and powerful development board. At its core is the ESP32-WROOM-32 module, featuring a dual-core Xtensa LX6 processor running at up to 240 MHz, supported by 520 KB of SRAM and 4 MB of flash memory. This enables robust performance for a wide range of embedded applications.
Wireless connectivity includes both Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth, with support for both Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), making the module ideal for IoT applications, remote monitoring, and smart device integration. On the wired side, the board includes a native CAN interface using the ESP32’s built-in TWAI (Two-Wire Automotive Interface) controller, paired with a 3.3 V CAN transceiver for seamless communication over the CAN bus.
The module supports classical CAN 2.0B communication at speeds up to 1 Mb/s and handles both standard (11-bit) and extended (29-bit) identifiers. It also provides features like programmable bit timing, acceptance filtering, and interrupt-driven operation, making it suitable for use in automotive diagnostics, industrial automation, and intelligent transport systems. More information...
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
