- Home
- Embedded Systems
- LPC1788 Development Board
Product Description
Free Shipping Within The United States!
The Open1788 module is an LPC development board designed for the LPC1788FBD208 microcontroller; it consists of the motherboard and the MCU core board Core1788.
The Open1788 supports expansion through various optional accessory boards for a specific application. The modular and open design makes it ideal for starting application development with the NXP LPC series microcontrollers.
Open1788 Board Components
- LPC1788FBD208 (core board):the high performance LPC MCU which features:
- Core: Cortex-M3 32-bit RISC
- Operating Frequency: 120MHz Max
- Operating Voltage: 2.4-3.6V (3.3V typical)
- Package: LQFP208
- I/Os: 165
- Memories: 512KB Flash, 96KB SRAM, 4K EEPROM
- MCU communication Interfaces:
- 1 x LCD, 1 x 10/100 ETH MAC, 1 x GP DMA Controller
- USB Device/Host (Onchip PHY and DMA Controller)
- 5 x UART, 3 x SSP, 3 x I2C, 1 x I2S, 2 x CAN,1 x SDIO
- 8 x 12Bit ADC, 1 x 10Bit ADC, 1 x DAC, 1 x MOTOR PWM
- 6 x GP PWM, 1 x Quadrature Encoder Interface, 1 x EMC
- AD & DA converters: 3 x AD (12-bit, 1μs, shares 24 channels); 2 x DA (12-bit)
- Debugging/Programming: supports JTAG/SWD (serial wire debug) interfaces, supports ISP via UART
- H57V1262GTR-75C (core board): 2PCS x 128M Bit SDRAM
- K9F1G08U0B (core board): 1G Bit NandFlash
- SST39VF3201 (core board): 32M Bit NorFlash
- LM3526-L (mother board bottom side): onboard USB power switch and over-current protection
- AMS1117-3.3, 3.3V voltage regulator
- Power supply switch
- Power indicator
- LEDs: convenient for indicating I/O status and/or program running state
- USB communication LED1: USB GOOD LINK1
- USB communication LED2: USB GOOD LINK2
- Reset button
- User key: convenient for I/O input and/or interact with running code
- Joystick: five positions
- 12M crystal oscillator (core board): used to boost operating frequency by frequency multiplication
- 32.768K crystal (core board), for internal RTC with calibration
- USB type A interface: for connecting USB devices such as USB flash drive
- CAN2 interface: communicates with accessory boards which feature the CAN device conveniently
- CAN1 interface: communicates with accessory boards which feature the CAN device conveniently
- AD+DA interface: for AD/DA testing
- USB OTG transceiver interface: for connecting USB OTG transceiver module
- SPI0 | SPI1 interface:easily connects to SPI peripherals such as DataFlash (AT45DBxx), SD card, MP3 module, etc.
- I2C1 | I2C2 interface: easily connects to I2C peripherals such as I/O expander (PCF8574), EEPROM (AT24Cxx), etc.
- I2S | I2C0 interface: for connecting I2S and/or I2C modules such as audio module, FRAM FM24CLxx, etc.
- Modem | UART1 interface: for connecting Modem and/or UART modules such as RS232, RS485, USB TO UART, etc.
- SDIO interface: for connecting Micro SD module, features much faster access speed rather than SPI
- Ethernet interface: easily connects the MCU to ethernet network by using an additional ethernet module, such as DP83848 Ethernet Board
- ISP | UART0 interface: for connecting ISP and/or UART modules such as RS232, RS485, USB TO UART, etc.
- ONE-WIRE interface: easily connects to ONE-WIRE devices (TO-92 package), such as temperature sensor (DS18B20), electronic registration number (DS2401), etc.
- LCD interface: for connecting to 4.3 inch touch screen LCD through an adapter
- USB mini interface: used for establishing USB communication between PC and the LPC development board
- 5V DC jack
- 5V/3.3 V power input/output: usually used as power output, also common-grounding with other user board
- MCU pins connector: all the idle pins are accessible on expansion connectors for further expansion
- JTAG/SWD interface: for debugging/programming
- LEDs jumper
- User key jumper
- Joystick jumper
- SD card detect jumper
- short the jumper to enable SD card detection function
- open the jumper to disconnect from I/O port
- USB enable jumper
- short the jumper to enable USB
- open the jumper to disconnect from I/O port
- USB HOST jumper
- short the jumper when using USB HOST
- open the jumper to disconnect from I/O port
- VBAT selection jumper
- short the jumper to use the onboard battery
- open the jumper to connect the VBAT to other external power
- VREFP selection jumper
- short the jumper to connect VREFP to VCC
- open the jumper to connect VREFP to other custom pin via jumper wire

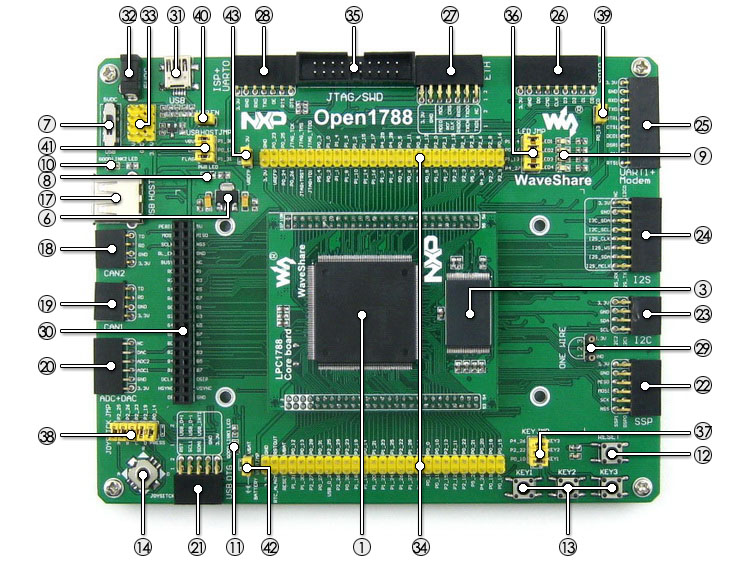
LPC1788 Development Board JTAG/SWD Interface
The following images show the header pinouts of the JTAG/SWD interface:

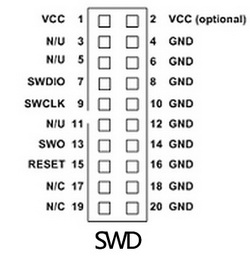
LPC1788 Development Board - Extension Boards
- CAN Bus Mini Breakout Board...
- DP83848 Ethernet Breakout Board...
- FT232 USB Micro UART Board...
- FT232 USB Mini UART Board...
- RS232 Board...
- RS485 Breakout Board 3.3 VDC...
- RS485 Breakout Board 5 VDC...
- Further Breakout Boards...
Development Resources
- LPC1788 Development Board - User Manual (PDF)...
- LPC1788 Development Board - Schematic (PDF)...
- Demo Code (7z)...
- LPC Software...
- LPC Design Resources...
MCUXpresso Integrated Development Environment (Free-of-charge):

In order to program the LPC1768 Development Board through the MCUXpresso IDE, the following components are required:
The Definitive Guide to ARM Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 Processors
by Joseph Yiu
 This new edition has been fully revised and updated to include extensive information on the ARM Cortex-M4 processor, providing a complete up-to-date guide to both Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 processors, and which enables migration from various processor architectures to the exciting world of the Cortex-M3 and M4.
This new edition has been fully revised and updated to include extensive information on the ARM Cortex-M4 processor, providing a complete up-to-date guide to both Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 processors, and which enables migration from various processor architectures to the exciting world of the Cortex-M3 and M4.
This book presents the background of the ARM architecture and outlines the features of the processors such as the instruction set, interrupt-handling and also demonstrates how to program and utilize the advanced features available such as the Memory Protection Unit (MPU).
Chapters on getting started with IAR, Keil, gcc and CooCox CoIDE tools help beginners develop program codes. Coverage also includes the important areas of software development such as using the low power features, handling information input/output, mixed language projects with assembly and C, and other advanced topics.
- Two new chapters on DSP features and CMSIS-DSP software libraries, covering DSP fundamentals and how to write DSP software for the Cortex-M4 processor, including examples of using the CMSIS-DSP library, as well as useful information about the DSP capability of the Cortex-M4 processor
- A new chapter on the Cortex-M4 floating point unit and how to use it
- A new chapter on using embedded OS (based on CMSIS-RTOS), as well as details of processor features to support OS operations
- Various debugging techniques as well as a troubleshooting guide in the appendix
- Topics on software porting from other architectures
- A full range of easy-to-understand examples, diagrams and quick reference appendices
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...







