Recent Posts
A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet - Introduction
Posted by on

The following is part of A Comprehensible Guide to Industrial Ethernet by Wilfried Voss.
Note: The term “Industrial Ethernet” needs further clarification as it may be interpreted as mere “Industrial-Strength” Ethernet. This book uses the term in reference to “Real-Time Industrial Ethernet” (For many engineers in the automation industry, “Industrial-Strength” is not possible without “Real-Time”).
The simple and effective design of the standard Ethernet TCP/IP protocol has made it the most popular networking solution at the physical and data link level, especially for general-purpose office networks. With high-speed options and a variety of available media types, Ethernet TCP/IP is efficient and flexible.
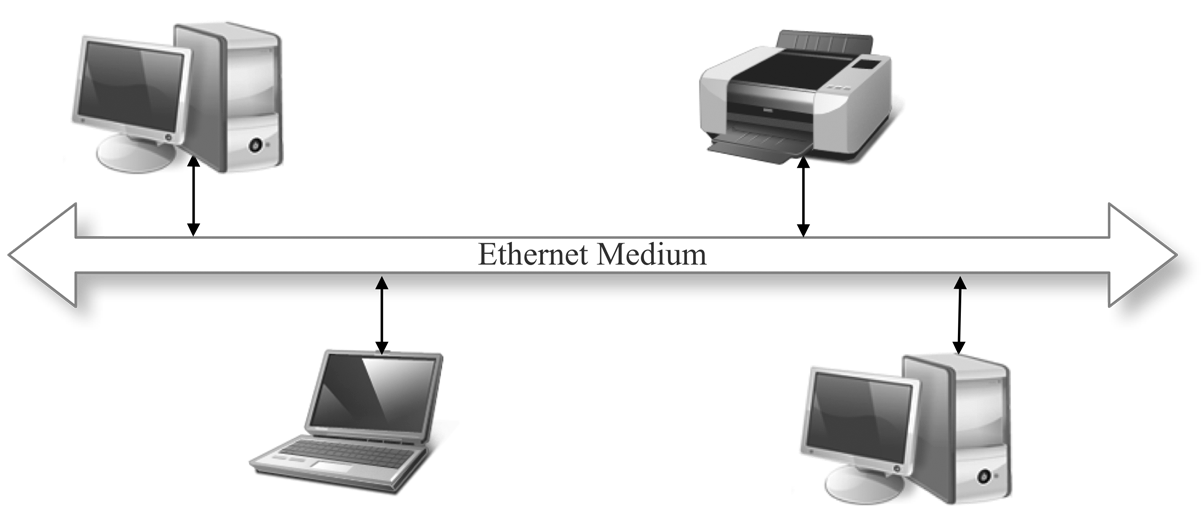
Ethernet Network Example
These factors and the lowering cost of Ethernet hardware have made Ethernet an increasingly attractive option for industrial networking applications. Also, Ethernet offers the possibility of a level of standardization and interoperability that has, until recently, remained elusive in the industrial field.
However, the unpredictable nature of Ethernet TCP/IP’s timing has long been a drawback for many industrial network applications, specifically those with real-time capability requirements. As the overall cost vs. benefit performance has improved over time, industrial users have developed methods to overcome the apparent shortcomings.
The implementation of additional Real-Time Data Exchange protocol layers (i.e., add-on software) incorporated prioritization, synchronization, and other techniques to ensure the timely delivery of messages. Also, the segmentation of networks through intelligent Ethernet Switches resolves the problem of bus congestion and message collisions to increase real-time capabilities.
Protocols such as EtherCAT®, ProfiNet V3, and Sercos III go even further by modifying the physical layer.
The result has been a booming application of Real-Time Industrial Ethernet for industrial control and automation applications. Industrial Ethernet is increasingly replacing established communication protocols at the plant floor level and even down to the cell and field levels.
EtherNet/IP: The Everyman’s Guide to The Most Widely Used Manufacturing Protocol
EtherNet/IP came roaring into the 21st century on the backs of DeviceNet and ControlNet, claiming world domination (almost) as the most widely used protocol in manufacturing.
While it’s pervasive, EtherNet/IP isn’t necessarily standard knowledge to everyone on the factory floor. Admit it; maybe you find yourself losing sleep over questions such as
- Is EtherNet/IP an IoT transport protocol?
- Are EDS files important for an EtherNet/IP adapter device?
- Which is better: EtherNet/IP or PROFINET IO?
- Isn’t EtherNet/IP just CIP over an Ethernet connection?
- How many ways are there to organize device data into a CIP Object Model?
- What is the Assembly Object Class?
- Can the EtherNet/IP encapsulation to encapsulate other automation protocols?
- Does it matter which TCP/IP stack we use to build an EtherNet/IP device?
- Is DeviceNet obsolete or complementary to EtherNet/IP? How important is the compliance test process?
- Is CoCO good for an EtherNet/IP scanner device, or delicious with marshmallows?
Toss and turn no more! With this handy guide on your bedside table, you’ll be able to navigate the world of EtherNet/IP and, who knows, maybe entertain a companion with exciting tidbits. Dip into any chapter, in any order, and you’ll find plenty of clear explanations, with tables and diagrams, to guide you through EtherNet/IP.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...

