Recent Posts
A Guide To Technologies And Techniques Required To Build Linux Into Embedded Systems
Posted by on
Embedded Linux runs many of the devices we use every day, from smart TVs to WiFi routers, test equipment to industrial controllers - all of them have Linux at their heart. Linux is a core technology in the implementation of the inter-connected world of the Internet of Things.
The comprehensive guide shows you the technologies and techniques required to build Linux into embedded systems. You will begin by learning about the fundamental elements that underpin all embedded Linux projects: the toolchain, the bootloader, the kernel, and the root filesystem. You'll see how to create each of these elements from scratch, and how to automate the process using Buildroot and the Yocto Project.
Moving on, you will find out how to implement an effective storage strategy for flash memory chips, and how to install updates to the device remotely once it is deployed. You'll also get to know the key aspects of writing code for embedded Linux, such as how to access hardware from applications, the implications of writing multi-threaded code, and techniques to manage memory in an efficient way. The final chapters show you how to debug your code, both in applications and in the Linux kernel, and how to profile the system so that you can look out for performance bottlenecks.
By the end of the book, you will have a complete overview of the steps required to create a successful embedded Linux system.
What you will learn
- Evaluate the Board Support Packages offered by most manufacturers of a system on chip or embedded module
- Use Buildroot and the Yocto Project to create embedded Linux systems quickly and efficiently
- Update IoT devices in the field without compromising security
- Reduce the power budget of devices to make batteries last longer
- Interact with the hardware without having to write kernel device drivers
- Debug devices remotely using GDB, and see how to measure the performance of the systems using powerful tools such as perk, ftrace, and valgrind
- Find out how to configure Linux as a real-time operating system
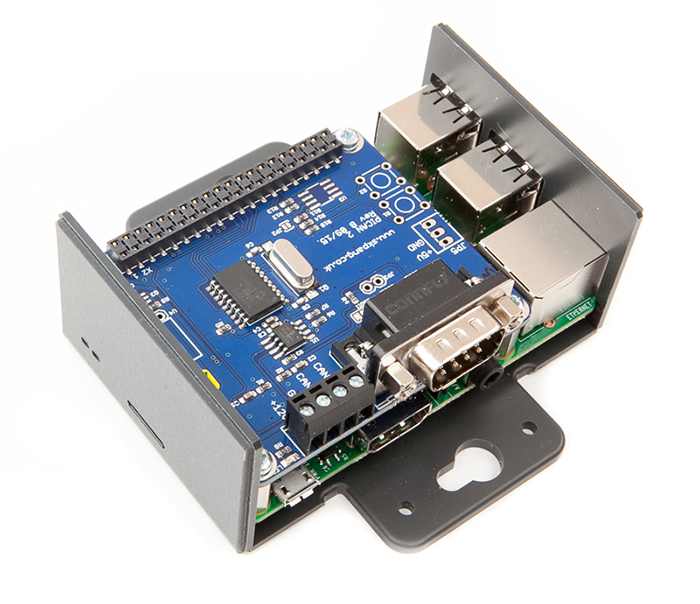
Raspberry Pi 3 System With CAN Bus Interface
Our Raspberry Pi 3 System With CAN Bus Interface (PiCAN2) comes with a pre-installed Raspbian operating system.
The PiCAN2 board provides Controller Area Network (CAN) Bus capabilities for the Raspberry Pi. It uses the Microchip MCP2515 CAN controller with MCP2551 CAN transceiver. Connection are made via DB9 or 3-way screw terminal.
There is an easy-to-install SocketCAN driver, and programming can be accomplished in C or Python.
The enclosure is a two part clip together plastic enclosure for use with the PiCAN2 board and the Raspberry Pi 2/3. The enclosure is made from High Impact Polystyrene HIPS UL94-HB material. Mounting flanges allow for wall mounting.
System Features
- Raspberry Pi 3, Model B, 1 GB RAM.
- Raspberry Pi 8GB Preloaded (NOOBS) SD Card - SanDisk Extreme 8GB microSDHC UHS-1 with speed up to 48 MB/sec.
- PiCAN2 - CAN Bus Interface for Raspberry Pi.
- The enclosure is made from High Impact Polystyrene HIPS UL94-HB material. Mounting flanges allow for wall mounting.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...