Recent Posts
Mapping the SAE J1939 Data Link Layer to CAN FD
Posted by on
About SAE J1939
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standard SAE J1939 is the vehicle bus recommended practice used for communication and diagnostics among vehicle components. Originating in the car and heavy-duty truck industry in the United States, it is now widely used in other parts of the world.
SAE J1939 is used in the commercial vehicle area for communication throughout the vehicle, with the physical layer defined in ISO 11898. A different physical layer is used between the tractor and trailer, specified in ISO 11992.
SAE J1939 defines five layers in the seven-layer OSI network model, and this includes the Controller Area Network (CAN) ISO 11898 specification (using only the 29-bit/"extended" identifier) for the physical and data-link layers. Under J1939/11 and J1939/15, the data rate is specified as 250 kbit/s, with J1939/14 specifying 500 kbit/s. The session and presentation layers are not part of the specification. The later use of CAN FD is currently discussed.
All J1939 packets, except for the request packet, contain eight bytes of data and a standard header which contains an index called Parameter Group Number (PGN), which is embedded in the message's 29-bit identifier. A PGN identifies a message's function and associated data. J1939 attempts to define standard PGNs to encompass a wide range of automotive, agricultural, marine and off-road vehicle purposes. A range of PGNs (00FF0016 through 00FFFF16, inclusive) is reserved for proprietary use. PGNs define the data which is made up of a variable number of Suspect Parameter Number (SPN) elements defined for unique data. For example, there exists a predefined SPN for engine RPM.
About CAN FD
Due to bandwidth requirements in the automotive industry, the CAN data link layer protocol needed improvement. In 2011, Bosch started the CAN FD (flexible data-rate) development in close cooperation with car makers and other CAN experts. The improved protocol overcomes two CAN limits: You can transmit data faster than with 1 Mbit/s and the payload (data field) is now up to 64 bytes long (i.e. it is not limited to 8 bytes).
In order to distinguish between classical data frames and CAN FD data frames, one of the previously reserved bits is used. This bit is called FDF (FD frame) bit. If it is of recessive value, and the following bit sequence is interpreted as a CAN FD data frame. If it is of dominant value, it is a classical data or remote frame. In the newly introduced BRS (bit rate switch) bit, the second bit-rate is applied, when it is of recessive (r) value. If it is of dominant (d) value, the arbitration phase bit-time setting is used in the data phase, too.
Mapping of J1939 to CAN FD
CAN-in-Automation (CiA) members have mapped SAE’s J1939 application profile to the CAN FD data link layer. The corresponding CiA 602-2 specification will be released soon.
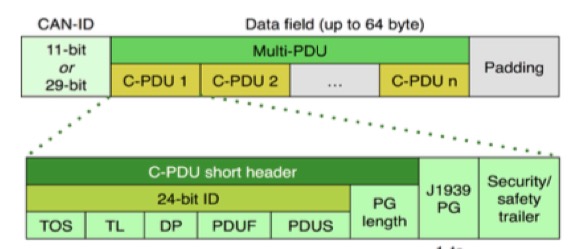
The J1939-21 application layer specifies the use of the CAN message ID and the protocol that transmits the Parameter Group Numbers (PGN). The PGNs and the single parameters are described in SAE J1939-71. Traditionally, the J1939 application profile is mapped to the Classical Extended Frame Format (CEFF) data link layer protocol using the 29-bit CAN-ID.
Some European OEMs of trucks need more bandwidth on their CAN-based in-vehicle networks. Additionally, they require higher throughput when downloading software or uploading diagnostic data. For this reason, some CiA members have started to specify the mapping of J1939 messages to CAN FD. It is intended to run the communication at higher bit-rates (e.g. 2 Mbit/s) and to use the extended payload of up to 64 byte.
=> Download the corresponding CiA application note (PDF)...
A Comprehensible Guide to J1939
SAE J1939 has become the accepted industry standard and the vehicle network technology of choice for off-highway machines in applications such as construction, material handling, and forestry machines. J1939 is a higher-layer protocol based on Controller Area Network (CAN). It provides serial data communications between microprocessor systems (also called Electronic Control Units - ECU) in any kind of heavy duty vehicles. The messages exchanged between these units can be data such as vehicle road speed, torque control message from the transmission to the engine, oil temperature, and many more.
The information in this book is based on two documents of the SAE J1939 Standards Collection: J1939/21 - Data Link Layer J1939/81 - Network Management A Comprehensible Guide to J1939 is the first work on J1939 besides the SAE J1939 standards collection. It provides profound information on the J1939 message format and network management combined with a high level of readability.
=> Read More...
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...

